High-Level Architecture for Implementing Zero Trust Vault on Stellar
Overview
This document outlines the high-level architecture for implementing the Zero Trust Vault Protocol on the Stellar blockchain using Soroban, Stellar's smart contract platform. The protocol leverages zero-knowledge proofs (ZK Proofs), RISC Zero zkVM, and Stellar's efficient payment and ledger infrastructure to create a trustless escrow system for high-value transactions.
Workflow
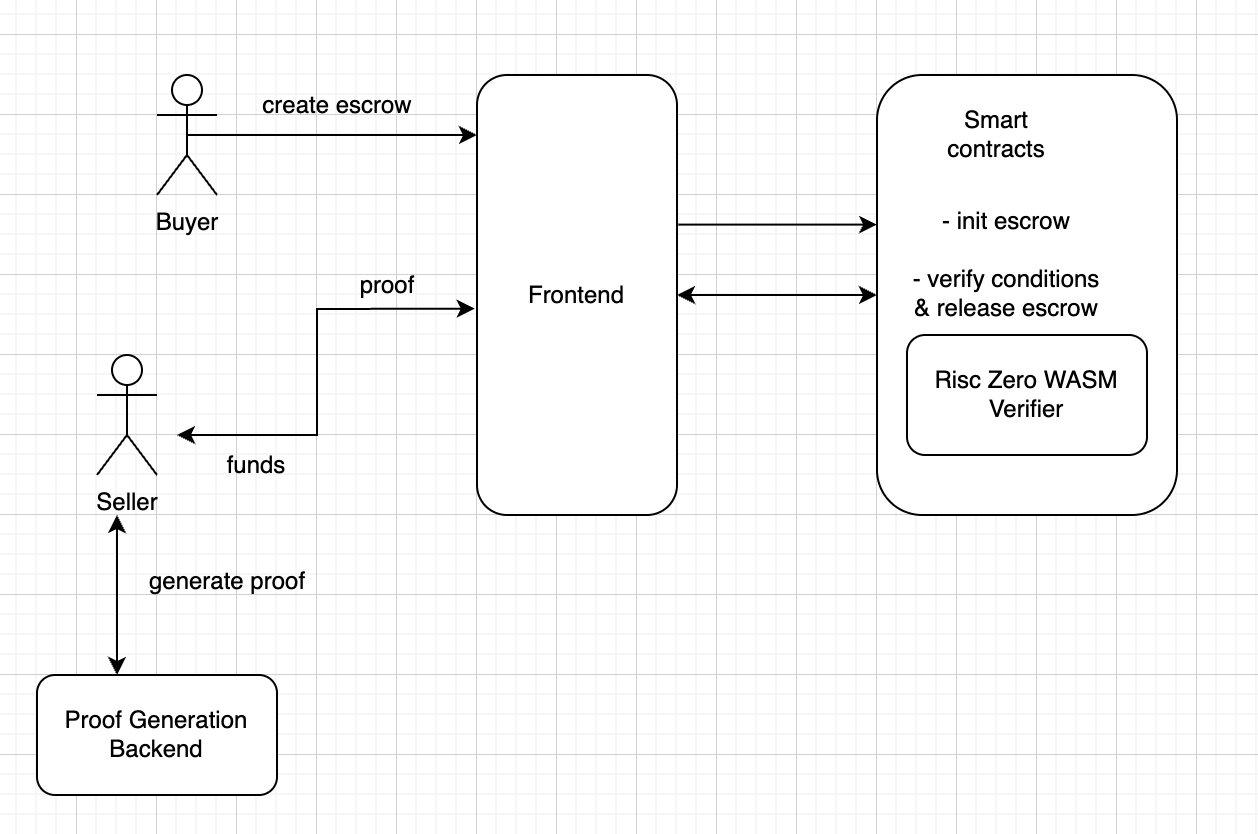
1. Escrow Creation
- The buyer initiates an escrow agreement through the frontend.
- The frontend generates the escrow details (buyer, seller, amount, conditions).
- The frontend interacts with the
Escrowsmart contract to lock the funds.
2. Condition Fulfillment
- The seller fulfills the agreement conditions.
- The seller or an external oracle generates a ZK proof off-chain using RISC Zero zkVM.
- The ZK proof is submitted to the
Risc Zero WASM Verifiersmart contract for verification.
3. Fallback Mechanism
- If a ZK proof cannot be supplied or is invalid:
- A DAO vote is triggered to resolve the dispute.
- DAO members vote via the frontend, and votes are tallied off-chain.
- The DAO's decision is submitted to the smart contract for final resolution.
4. Fund Release
- If conditions are fulfilled (via ZK proof or DAO decision):
- The contract releases funds to the seller.
- If conditions are unmet:
- The contract refunds the buyer.
Key Components
1. User Interface (Frontend)
- Purpose: Provide an intuitive way for users to interact with the escrow system.
- Technologies:
- Framework: React.
- Libraries: Stellar SDK for payments and wallet integrations.
- Wallet Integration: Albedo, Freighter, or Rabet for signing Stellar transactions.
- Key Features:
- Create and manage escrow agreements.
- Submit ZK proofs or trigger fallback mechanisms.
- View escrow statuses and DAO voting interfaces.
2. Backend Services
- Purpose: Act as a bridge between the frontend, Soroban smart contracts, and off-chain ZK proof generation.
- Technologies:
- Frameworks: NestJS (Express) server as entrypoint; Rust SDK integration for Risc Zero Bonsai interaction
- Responsibilities:
- Off-chain generation of ZK proofs using RISC Zero zkVM.
- Relaying proofs and other inputs to the Soroban smart contracts.
- Handling off-chain DAO voting mechanisms (optional).
- Components:
- Proof Generation Service:
- Generates ZK proofs based on user-provided data.
- Ensures proofs adhere to the escrow agreement conditions.
- Proof Generation Service:
3. ZK Proof Verification
- Purpose: Leverage RISC Zero zkVM for privacy-preserving condition verification.
- Technology: WASM-based RISC Zero Verifier. (Non-existent yet, needs to be implemented)
- Workflow:
- Proof Generation:
- Users generate ZK proofs off-chain using RISC Zero zkVM.
- Proofs are submitted on-chain to the WASM Risc Zero Verifier contract for verification.
- On-Chain Verification:
- The smart contract uses the RISC Zero verifier in WASM to validate the submitted proofs.
- If valid, the escrow conditions are considered fulfilled, and funds are released.
- Proof Generation:
4. Smart Contracts
- Purpose: Implement the escrow logic, proof verification, and fund management.
- Technology: Rust with the Soroban SDK.
- Responsibilities:
- Lock funds in escrow upon agreement creation.
- Validate ZK proofs using the WASM RISC Zero zkVM verifier.
- Trigger fallback DAO-based dispute resolution if proof verification fails or conditions are unmet.
- Release funds to the appropriate party upon agreement fulfillment or dispute resolution.
- Key Contracts:
- Escrow Contract:
- Stores escrow details (buyer, seller, amount, conditions).
- Handles locking, releasing, and refunding funds.
- DAO Dispute Resolver: DAO Voting Service:
- Collects and tallies DAO member votes for fallback scenarios.
- Submits the final vote result to Soroban contracts.
- Enforces fairness and transparency in fallback scenarios.
- Escrow Contract:
Deployment and Hosting
1. Frontend
- Host on decentralized platforms like IPFS or traditional CDNs like AWS CloudFront.
2. Backend
- Deploy on cloud providers (AWS, GCP, Azure) or containerized environments (Docker, Kubernetes).